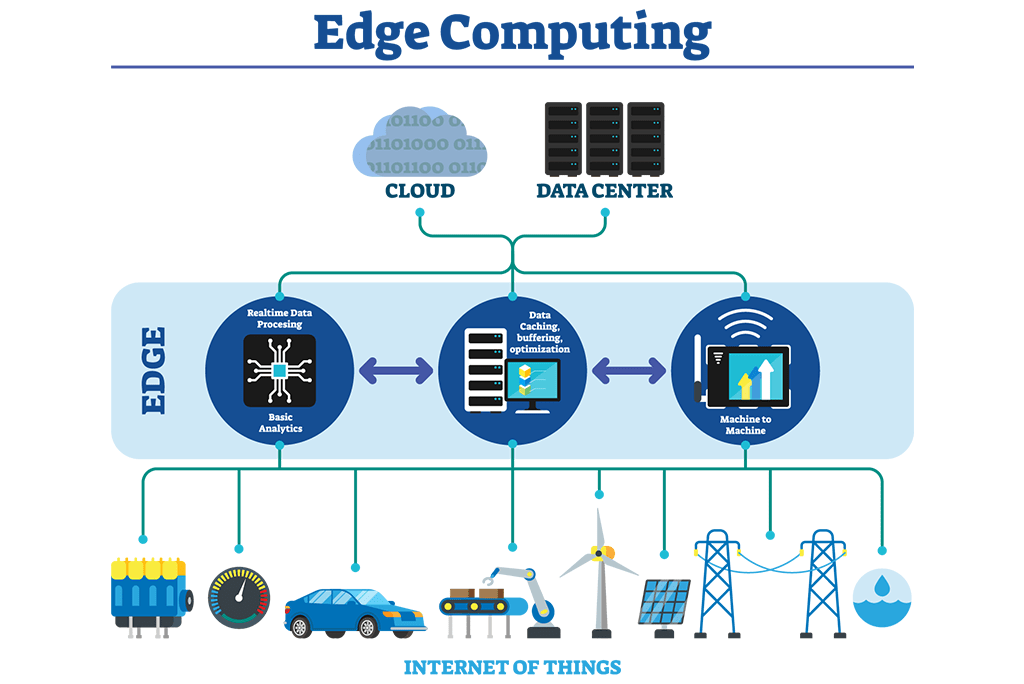
Have you ever wondered how much our digital world relies on the speed and efficiency of data processing? In an age where technology continually advances, edge computing has emerged as a game changer, shaping how applications perform and interact with users. Let’s take a closer look at this innovative approach and how it can transform modern applications.
Understanding Edge Computing
As we generate more data through various devices, from smartphones to IoT sensors, traditional centralized computing systems can struggle to keep up. Edge computing addresses this challenge by bringing computation and data storage closer to the location where it’s needed. This minimizes latency and bandwidth use, which can greatly enhance performance.
What Sets Edge Computing Apart?
Unlike cloud computing, which relies on remote servers to process data, edge computing processes data on local devices or nearby servers. This means that decisions can be made quickly without needing to send data back and forth to a centralized system. Imagine playing an online game where your moves are processed in real-time, providing a smooth and responsive experience. That’s the magic of edge computing.
Benefits of Edge Computing
There are several compelling benefits that edge computing brings to the table:
-
Reduced Latency: By processing data closer to the source, responses are quicker. This is particularly important for applications where speed is critical, such as in autonomous vehicles or smart manufacturing.
-
Bandwidth Efficiency: Since edge computing minimizes the need to send large amounts of data to the cloud, it significantly reduces bandwidth consumption, which can save on costs and improve service reliability.
-
Enhanced Security: Keeping sensitive data closer to the source can help reduce exposure to potential cyber-attacks. While no technology is entirely foolproof, localized data management can increase security.
-
Improved Reliability: In situations where network connectivity might be sporadic, edge computing allows devices to continue functioning and processing even when they’re offline or partially connected.
Use Cases of Edge Computing
Understanding edge computing becomes clearer when we dive into its applications. Here’s where edge computing is making a substantial impact:
1. Smart Cities
In the burgeoning concept of smart cities, edge computing plays a vital role. Sensors monitoring traffic, pollution levels, and public safety generate massive amounts of data. Processing these data points at the edge allows for real-time analysis, enabling city planners to make quick decisions that enhance public services and improve citizens’ quality of life.
2. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars rely on a myriad of sensors and cameras to gather data about their surroundings. With edge computing, these vehicles can process that information instantaneously, allowing them to make split-second decisions. This capability is crucial for ensuring safety on the roads.
3. Healthcare
In healthcare, edge computing can transform patient care. Wearable health devices can monitor vital signs and transmit data to healthcare providers instantly. This leads to faster responses in emergencies and better healthcare outcomes by utilizing real-time data analysis.
4. Retail
Retailers have begun leveraging edge computing to enhance the shopping experience. Applications can analyze customer behavior and inventory levels in real-time, leading to more personalized marketing and improved stock management. Not to mention, this technology also helps in managing security measures.
How Edge Computing Works
I find it fascinating to look at the mechanics behind edge computing. Essentially, it consists of various components that work together seamlessly to ensure efficient data processing.
Components of Edge Computing
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Edge Devices | These are local devices such as sensors, gateways, and IoT devices that collect data. |
| Edge Nodes | More powerful computing resources located near the edge. They handle complex processing tasks. |
| Data Management | Strategies to ensure data is properly processed, stored, and analyzed at the edge. |
| Network Infrastructure | Offers connectivity among devices, nodes, and cloud services. |
Each of these components plays a crucial role, working together to create a framework that optimizes data processing for modern applications.
The Edge vs. the Cloud
It’s important to understand how edge computing differs from cloud computing. While both paradigms have their advantages, they serve different needs. Here’s a side-by-side comparison to clarify:
| Feature | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Low (real-time processing) | Higher (dependent on connection speed) |
| Bandwidth Usage | Low (local processing) | High (data sent to and from cloud) |
| Data Security | More secure (local data handling) | Vulnerable to remote access and breaches |
| Reliability | More reliable in unstable networks | Can be affected by connection issues |
| Cost | Can save costs on bandwidth | May incur higher long-term data storage costs |
From what I’ve read, leveraging the strengths of both edge and cloud computing can yield powerful synergies for applications that need to balance latency, bandwidth, and processing power.
Challenges of Edge Computing
While edge computing offers numerous advantages, it’s not without its challenges. I feel it’s essential to be aware of these hurdles so we can find ways to overcome them.
1. Management Complexity
Managing a decentralized network of edge devices can become complex. As more devices come online, maintaining and overseeing these operations can require sophisticated management tools and practices.
2. Security Concerns
While localized data processing can enhance security, it also creates more endpoints that can be vulnerable to cyber threats. Each edge device represents a potential attack surface, making it crucial for organizations to adopt strong security measures.
3. Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating edge computing into existing IT infrastructure can pose significant challenges. Organizations often rely on legacy systems, and ensuring compatibility can be a daunting task. Developing a strategy for seamless integration is essential for success.
The Future of Edge Computing
When I think about the future, I see edge computing expanding its influence across various sectors. With the growth of IoT and the ongoing need for real-time data processing, it’s hard to ignore the impact edge computing might have.
Trends on the Horizon
-
5G Technologies: The rollout of 5G networks will further enable edge computing by providing ultra-fast connections with low latency. This will open new opportunities for applications, particularly in areas like augmented reality and connected devices.
-
AI and Machine Learning: As AI continues to evolve, its integration at the edge will allow for smarter, more autonomous operations. Devices will not only process data but also learn and adapt based on user interactions.
-
More Regulatory Focus: As more businesses harness the power of edge computing, regulatory frameworks will likely emerge to address data privacy and security. Organizations will need to stay informed about these regulations to ensure compliance.
Building an Edge Computing Strategy
As I ponder how to implement edge computing effectively, I recognize several key steps organizations can take to build a robust strategy.
1. Assess Organizational Needs
I recommend starting with a thorough assessment of the organization’s specific needs. By identifying where latency and bandwidth issues are felt the most, businesses can understand where edge computing is likely to provide the most benefit.
2. Choose the Right Technology
There’s an array of technologies to consider when implementing edge computing. Organizations should evaluate their existing IT infrastructure and determine which edge solutions best fit their use case.
3. Security Measures
Incorporating strong security measures is paramount. This involves not only securing the data itself but also ensuring edge devices and networks are protected from potential threats.
4. Pilot Programs
Implementing pilot programs can help businesses test edge computing without a full-scale commitment. This approach allows organizations to gather feedback and assess effectiveness in real-world scenarios.
5. Continuous Evaluation
Lastly, it’s vital to maintain a mindset of continuous evaluation. As technology evolves and new challenges arise, regularly revisiting the strategy will help ensure it remains aligned with changing organizational goals.
Conclusion
The power of edge computing in modern applications is undeniable. The way this technology enables faster processing, enhances security, and improves efficiency opens up a world of possibilities. As I think about its future, especially in tandem with trends like 5G and AI, I cannot help but feel optimistic.
By harnessing the capabilities of edge computing, businesses can position themselves for success in an increasingly digital world. It’s up to us to embrace this technology, adapt to its challenges, and fully realize its potential.
In a world that thrives on speed and efficiency, understanding and implementing edge computing can be a turning point for many organizations. As we continue forward, I look forward to seeing the ways this technology reshapes our interactions and experiences in the digital landscape.